PCBs in Schools: A Hidden Environmental Hazard
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were banned in 1979, yet many schools constructed between 1950 and 1980 still contain them. Despite being out of production for decades, PCBs remain a persistent environmental hazard due to their durability and widespread use in building materials such as caulking, adhesives, and fluorescent light ballasts. It is estimated that between 25% and 50% of the 48,000 U.S. schools built or renovated between 1950 and 1979 may have used materials containing PCBs. (Source: Managing PCBs in Schools, Western States PEHSU Fact Sheet, 2017).
PCBs are known to degrade indoor air quality and pose significant health risks, particularly in older school buildings. These compounds are slow to break down in the environment and can accumulate in the human body over time, potentially causing long-term health effects such as developmental issues, immune system suppression, and cancer.
The Prevalence of PCBs in Schools
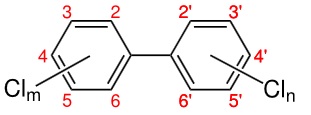
*Structure of polychlorinated biphenyl.
PCBs were widely used in building materials during the mid-20th century due to their insulating properties and chemical stability. As a result, many schools constructed between 1950 and 1980 still contain PCB-laden materials such as:
- Caulking and Sealants: Used around windows, doors, and other structural joints.
- Fluorescent Light Ballasts: Common in lighting fixtures installed during this period.
- Paints and Coatings: Applied to walls and surfaces for durability.
- Adhesives: Found in construction materials and flooring systems.
Studies conducted by environmental agencies have shown that a significant number of older schools still harbor PCBs, often unknowingly. Over time, these materials can deteriorate, releasing PCBs into the air, dust, and surrounding environment. Poor ventilation in older buildings exacerbates the problem, allowing PCB concentrations in indoor air to reach unsafe levels.
The issue is widespread, as many schools built during this era have not undergone comprehensive renovations or replacements of PCB-containing materials. Budget constraints and lack of awareness have often delayed necessary updates, leaving these hazardous materials in place. Additionally, testing for PCBs is not uniformly required, which means contamination often goes undetected until major maintenance projects are undertaken. Identifying and addressing PCB prevalence in schools is essential for ensuring the safety of students and staff. Through proactive measures such as routine testing and targeted remediation, schools can mitigate risks and create healthier indoor environments for all occupants.
Health Risks of PCBs in Indoor Air
Exposure to PCBs in indoor air can lead to a range of health concerns, especially for vulnerable populations such as children. Short-term exposure to high levels of PCBs may cause skin conditions like chloracne or rashes, while prolonged exposure has been linked to more severe effects, including:
- Developmental Delays: PCBs can interfere with brain development in children, leading to cognitive and behavioral issues.
- Endocrine Disruption: These compounds can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially affecting growth and reproduction.
- Immune System Impairment: PCBs can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Cancer Risk: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies PCBs as probable human carcinogens, linked to increased risk of liver and other cancers.
The risk of PCB exposure becomes even more critical during renovations, maintenance, or demolition activities, which can release PCBs trapped in building materials into the air and dust. Without proper environmental testing, these activities can inadvertently increase exposure risks for students, teachers, and maintenance staff. Environmental testing for PCBs in indoor air is essential for identifying contamination and ensuring safe learning environments. By proactively assessing and addressing potential PCB hazards, schools can protect the health and well-being of their occupants while complying with regulatory standards. Implementing routine testing and mitigation strategies demonstrates a commitment to maintaining a safe and healthy educational environment for all.
At Teklab, we understand that environmental compliance and testing can be complex. Our team is here to assist you in navigating regulations and ensuring a safe environment. Contact us today for expert PCB air testing solutions. Call (618) 344-1004 direct or Toll-Free at (877) 344-1003. View Teklab’s Certification for TO-10/13/15 – LELAP. For full details on the EPA/NERL PCB in Schools study, refer to: PCBs in School Buildings: Sources, Environmental Levels, and Exposures (2012).
-Learn more about PCBs in building materials on the EPA website.



